This week’s teacher feature highlights an infant class’s adventure to the Kenneth E. Behring Family Hall of Mammals at the National Museum of Natural History. The teachers, Erica Collins, Katherine Schoonover, and Noel Ulmer, paired the museum excursion with the book “Polar Bear, Polar Bear, What do you Hear?” by Bill Martin Jr. and Eric Carle. While this experience was carefully planned and curated by the teachers, the infants’ interests ultimately determined which animals the class focused on. By intentionally responding to their class’s cues, the teachers allowed the infants to lead the lesson based on individual interests. Below you will find images from the day as well as a reflection from the teachers.
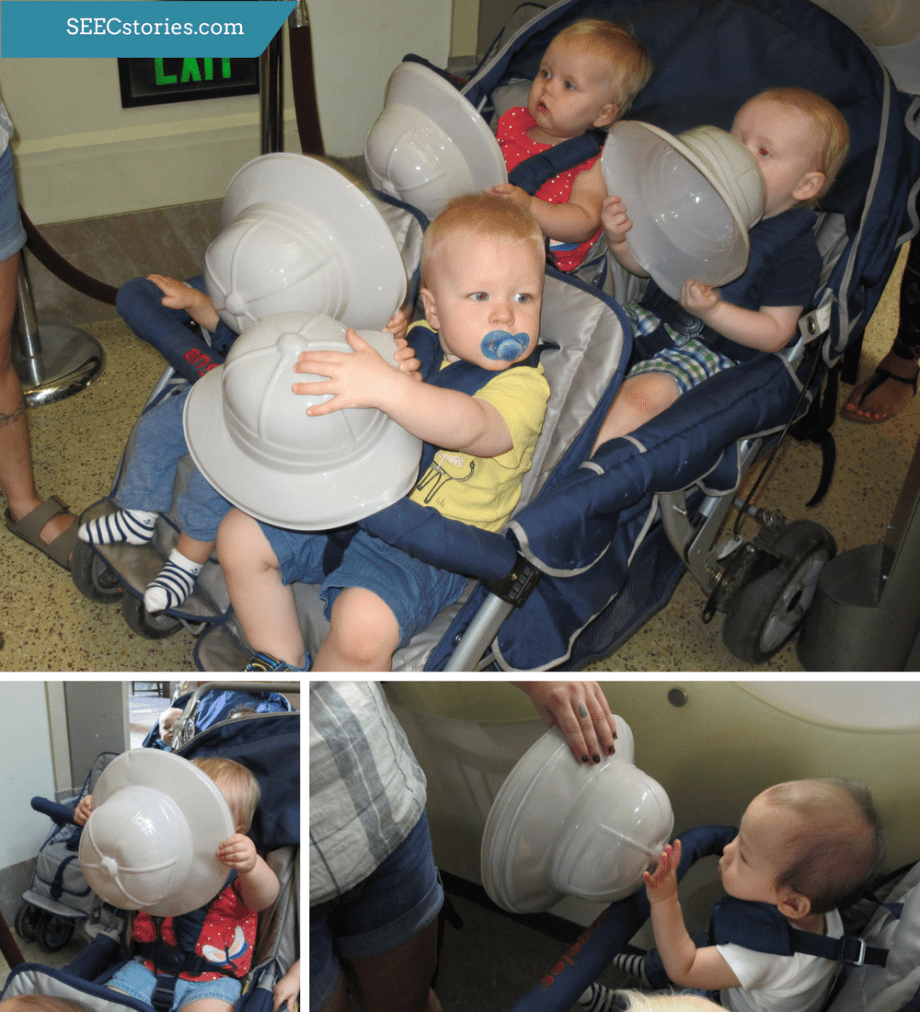


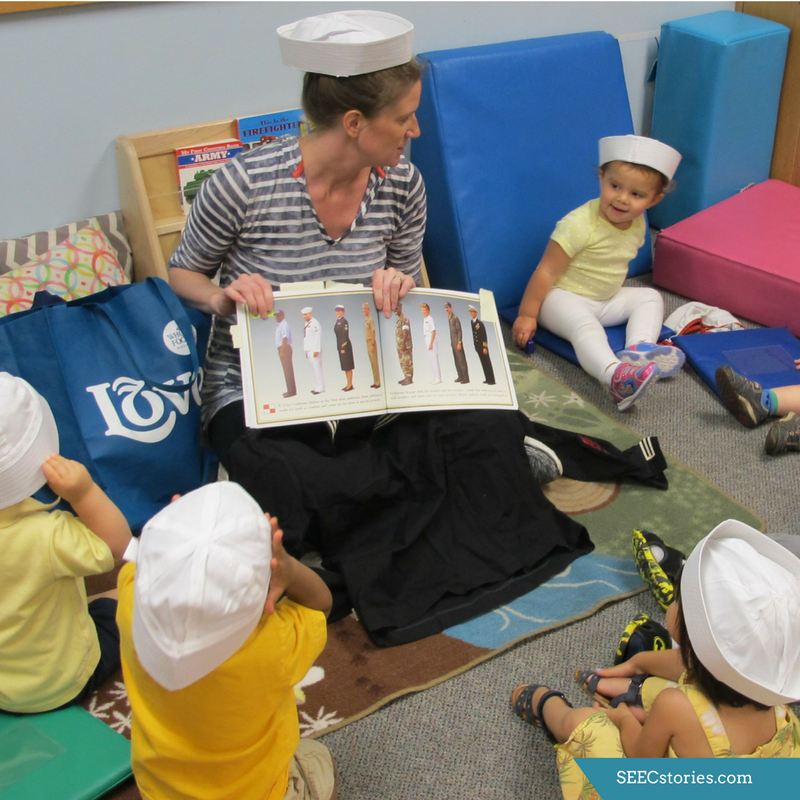
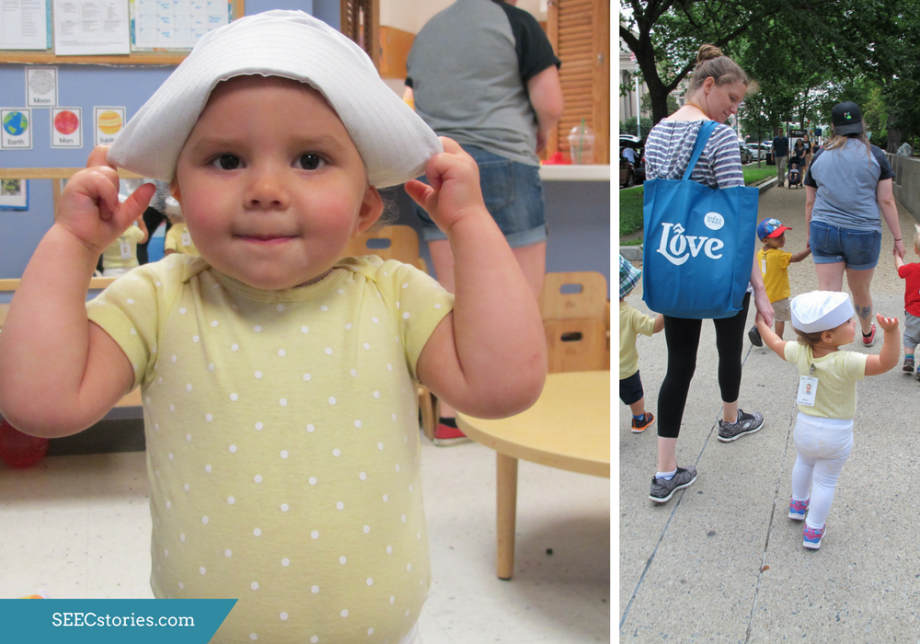
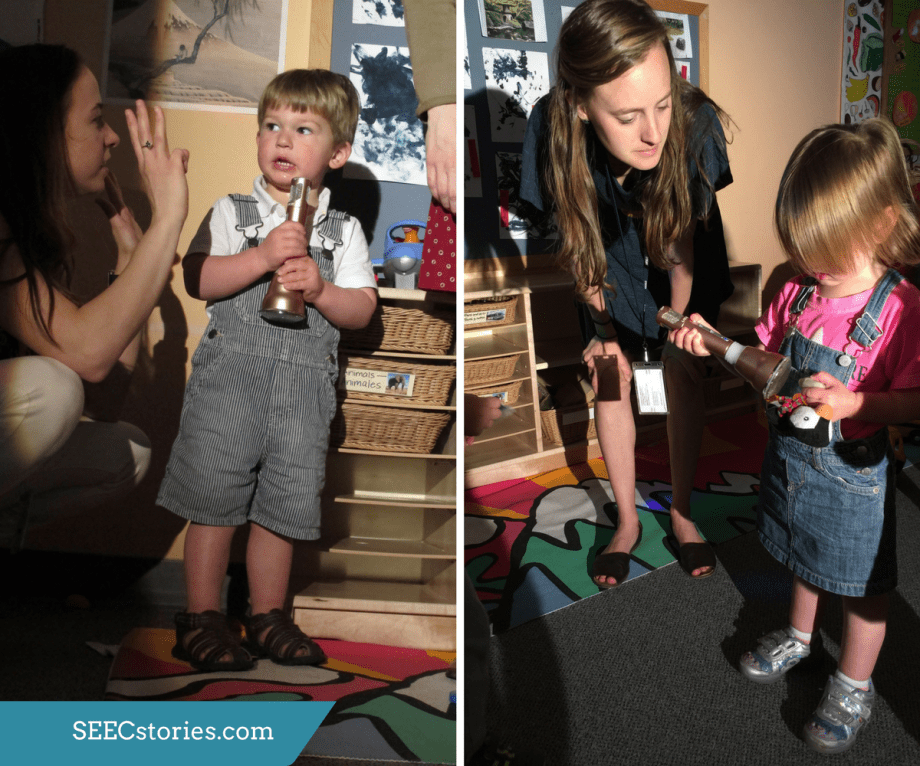
To start their adventure, the teachers passed out safari hats. Each child was given the opportunity to touch and explore the hats. Many tried putting the hats on, taking the hats off, and even experimented with covering their eyes with the hats. In addition to something new to hold, the hats also served as a transitional object to ease the move from the classroom and to the mammal hall.
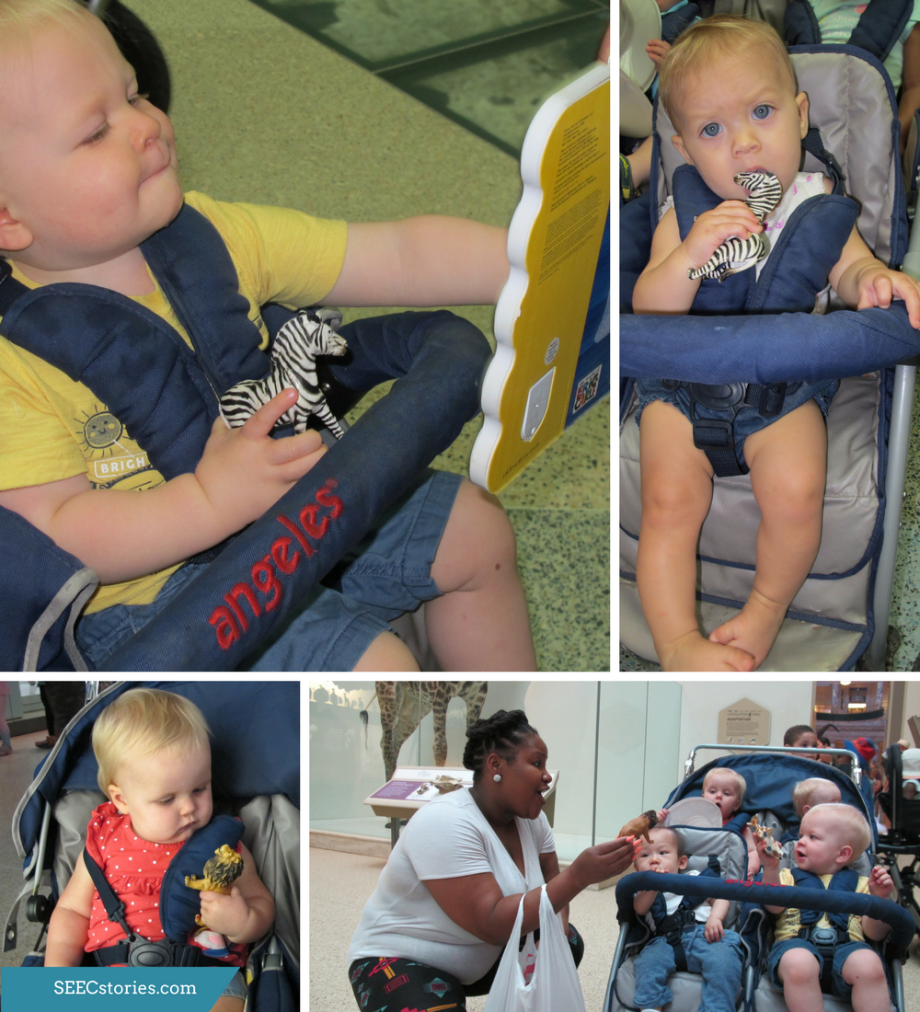

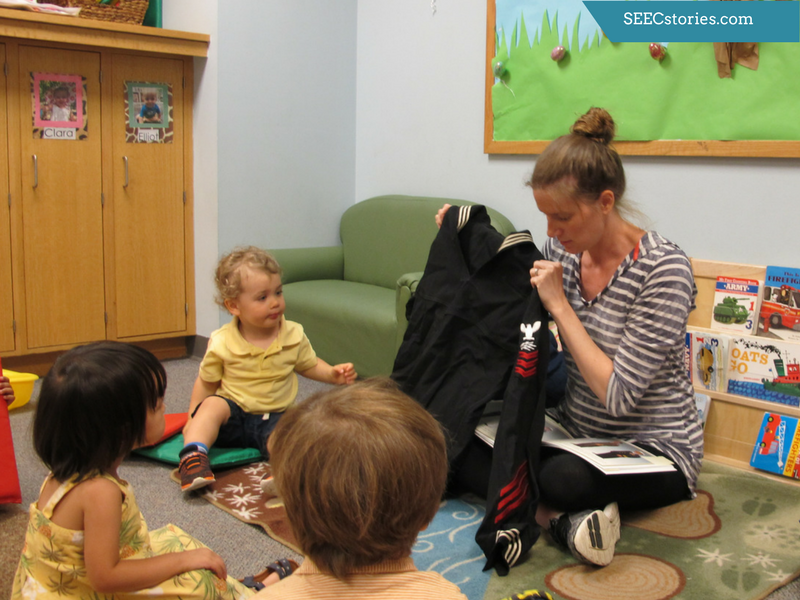
While in the mammal hall, the children were able to hold animal figurines that matched the animals that they saw in the mammal hall and in the book Polar Bear, Polar Bear, What do you hear? These animals helped the teachers personalize the lesson as they could take note of which animal each child was most interested in based on the animal that the children chose to hold.

For these young children, the book itself was an object. They were excited to be able to touch, hold, explore, and even push buttons to make noise. The book, which the class had been reading regularly, helped bridge the gap from the familiar to the unfamiliar large animals.
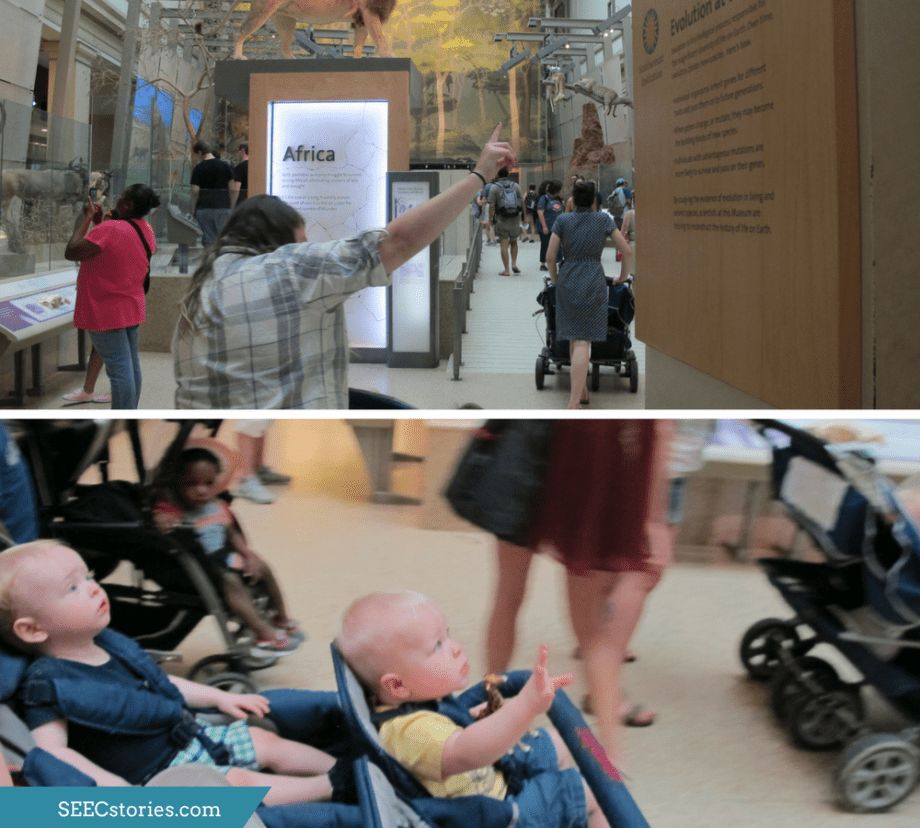

Most of the children in this class are preverbal, but this does not mean that they are unable to communicate. In fact, the infants use their physical activity to communicate by pointing and making gestures. The teachers were careful to narrate everything they saw and also communicated with gestures while paying careful attention to the children.
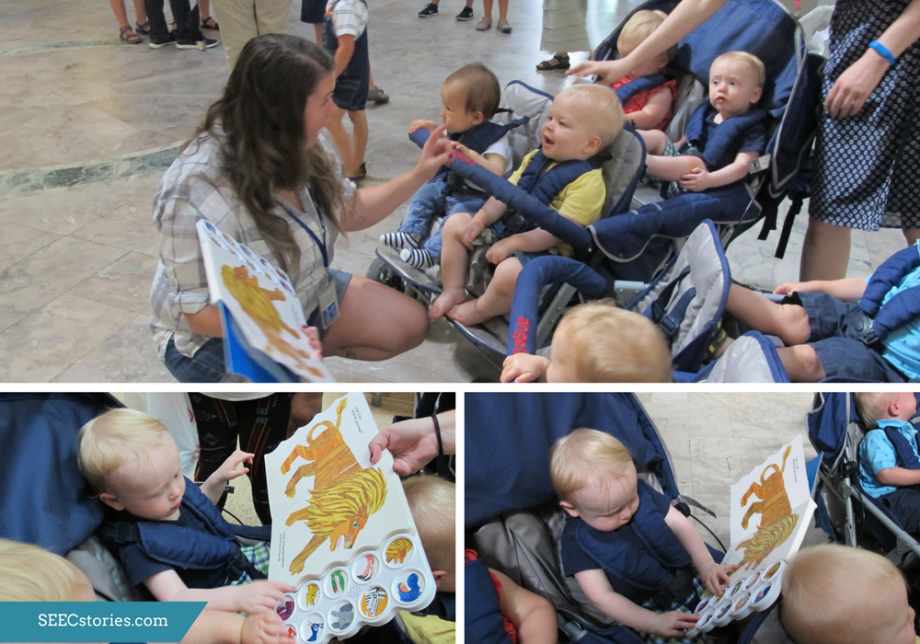

Another way the teachers were responsive to the class was by rotating who held the book Polar Bear, Polar Bear, What do you Hear? If a child expressed interest in looking closer at the book, the teachers would bring the book over to that child. If that child wanted to hold the book and explore it on his or her own, the teachers responded to the wants and needs of the individual by giving the child the opportunity to hold the book on his or her own while the rest of the class observed some of the mammals.

The book, Polar Bear, Polar Bear, What do you Hear?, focuses on the sounds that the different animals make and young children love experimenting with the different sounds they can make. This makes for a perfect pair. While in the mammal hall, the children attempted to mimic the sounds that different animals make.
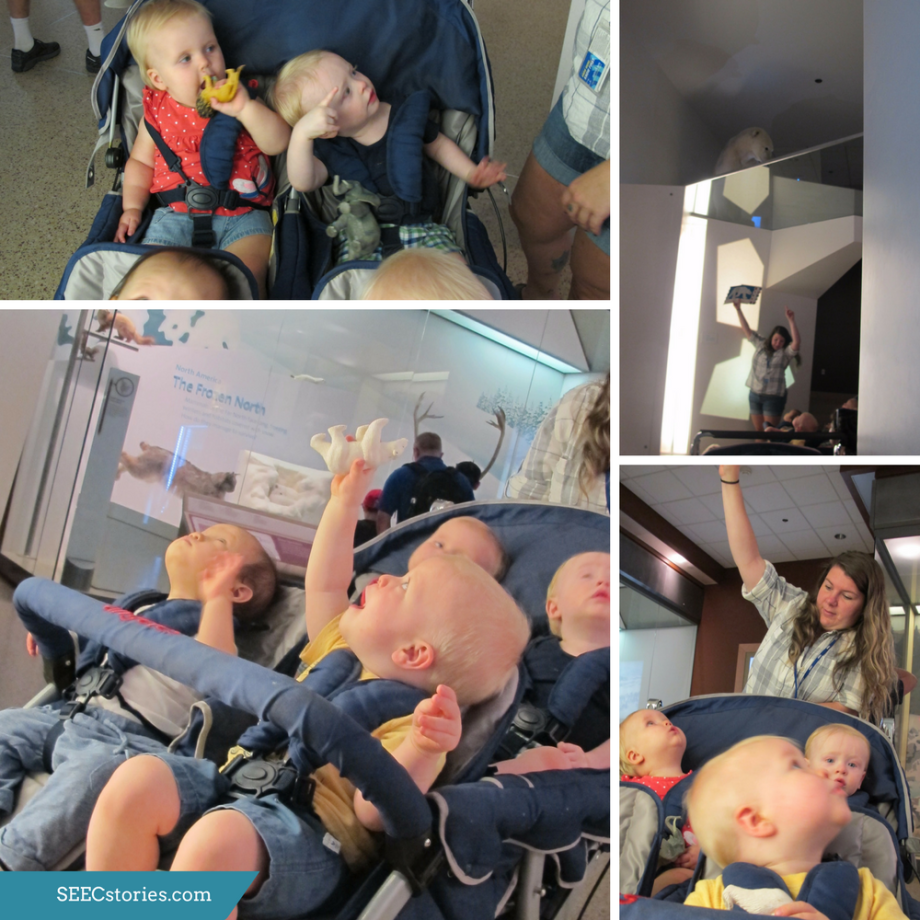

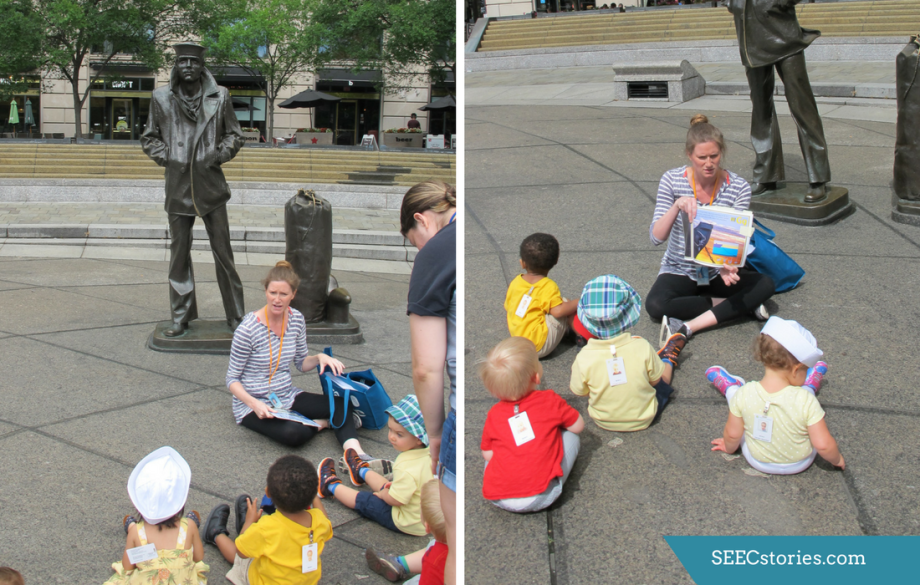
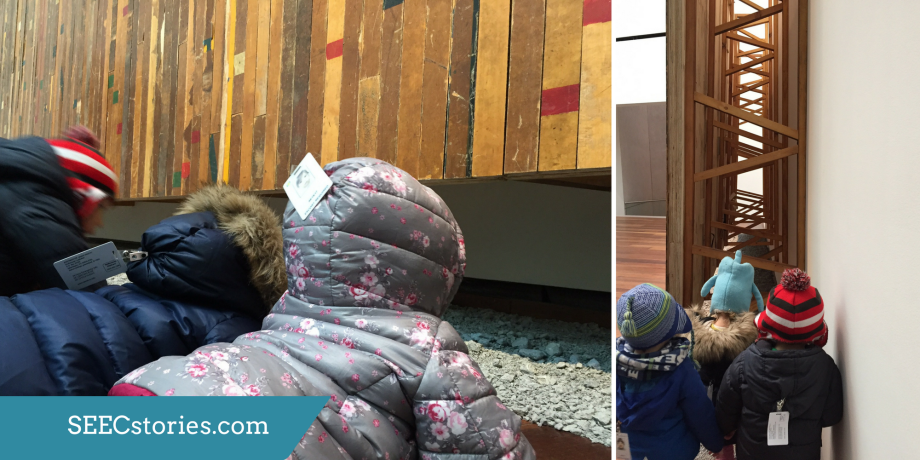
The last stop on their adventure was to see the polar bear, which is on display up high. The children were captivated by the polar bear and craned their necks upward to get a better view.
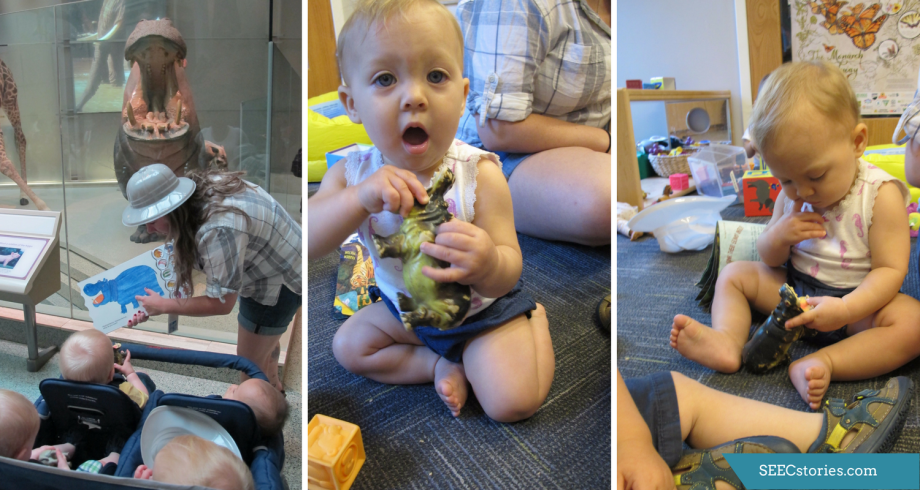
Back in the classroom, the teachers were able to continue assessing which animals the children wanted to explore further. The children gravitated towards certain animals. In the picture above, you can see one child actively exploring the teeth of the hippopotamus, which she had seen earlier in the mammal hall, and comparing them to her own teeth.
A reflection from Erica, Katherine, and Noel:
Preparation
We began learning about animals by exploring the different ways they look, sound, and move. This topic started to emerge within our classroom when the students began to recognize animals and mimicked the sounds animals make to let us know that they had noticed a specific animal. We wanted to show our class these animals up close and personal and to relate them to the books we see them in, the songs we sing about them, and the images of different mammals we encounter every day. Choosing to go to the mammal hall made the most sense since the animals there are so lifelike, other than they don’t make noise, but luckily the students helped us with that. We took safari hats with us to wear as we searched for our favorite animals and the animals mentioned in the book Polar Bear Polar Bear What Do You Hear? We wanted the students to come away from the lesson having made the connections between what they saw and heard in one of their favorite books to the size and shape of the animals in the mammal hall. In preparation for this lesson, we did many different kinds of movement in the classroom to mimic animal movements and often demonstrated the sounds these animals make.
Lesson
The most effective part of our lesson was showing the students the connection between the animals on the page and the animals in the mammal hall. Creating space for the students to get a sense of how big the animals are helped to expand this topic. Viewing the images of animals on a page, then seeing them in person, and then still being able to connect to the of sound of animals is pretty significant. Our time spent preparing in the classroom and going over the different animals made the lesson smoother. Rather than overwhelming the children with all the massive animals, we gave them time to adjust to each animal. Some students even had favorites, which we had planned to focus on. We were surprised to see which students were really engaged as we went through the mammal hall. Some students, who we had expected to be very vocal because they growl and make lion noises all day, were relatively quiet. We think they saw how lifelike and big a real lion was when we got up close and they were so entranced that they stopped growling and making noise which none of us expected to happen.
Reflection
Avoiding crowds is always something that is hard to manage, especially in the mammal hall, because it attracts so many people. The book we brought with us also had buttons for each animal to make noise, but it was so crowded that it was hard to hear at times. Luckily, our class had been pushing these buttons for weeks, so they were still able to make the connection even without us using the sounds in the book. After completing our safari hunt through the mammal hall, we continued to look at different animal books, wear our safari hats, and make observations about different animals.
If we were to do this lesson again, we would spend more time discussing all types of animals rather than just mammals. We would also focus on what makes different animals distinct from each other. We believe that looking at more types of animals (reptiles, birds, etc.) would not have hindered the students’ exploration of the mammals, but rather it would have opened up the topic to more discussion and learning.
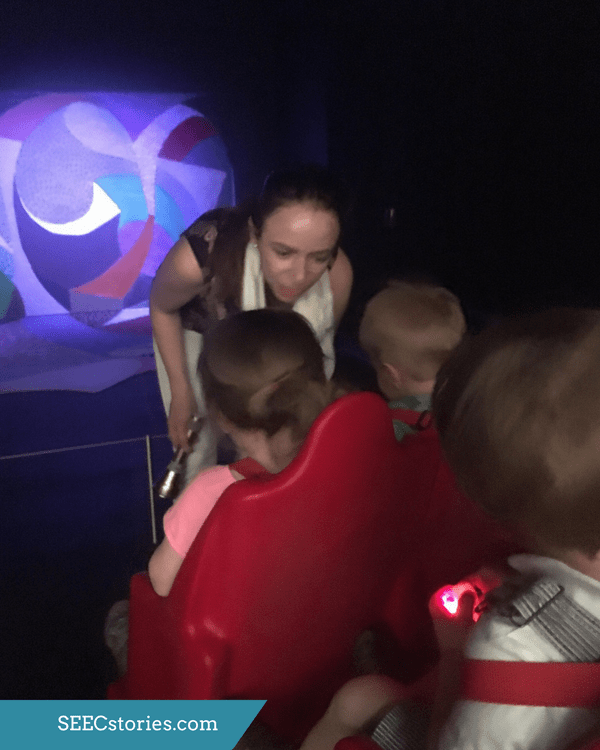
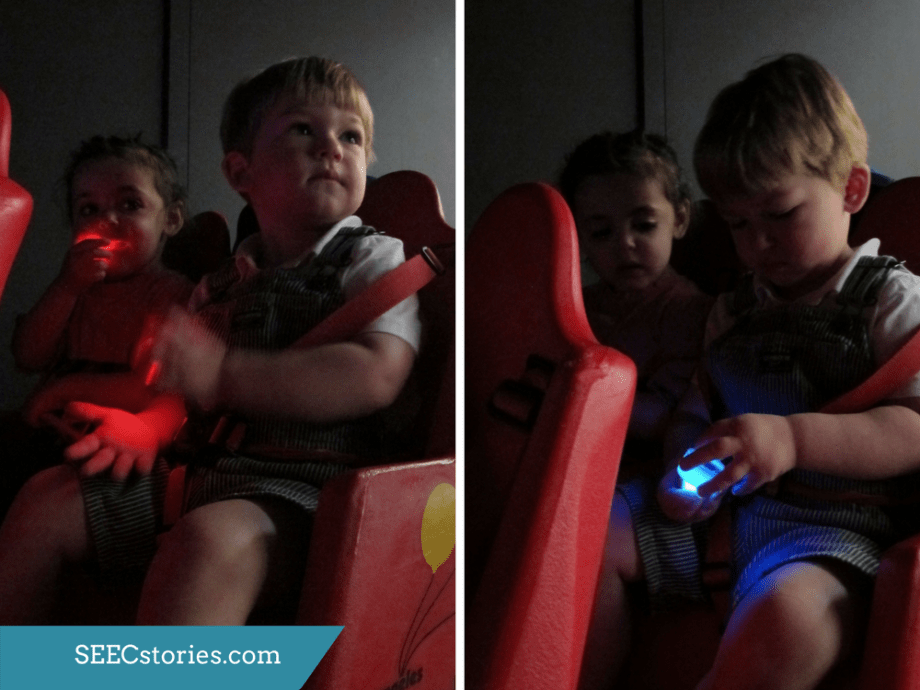












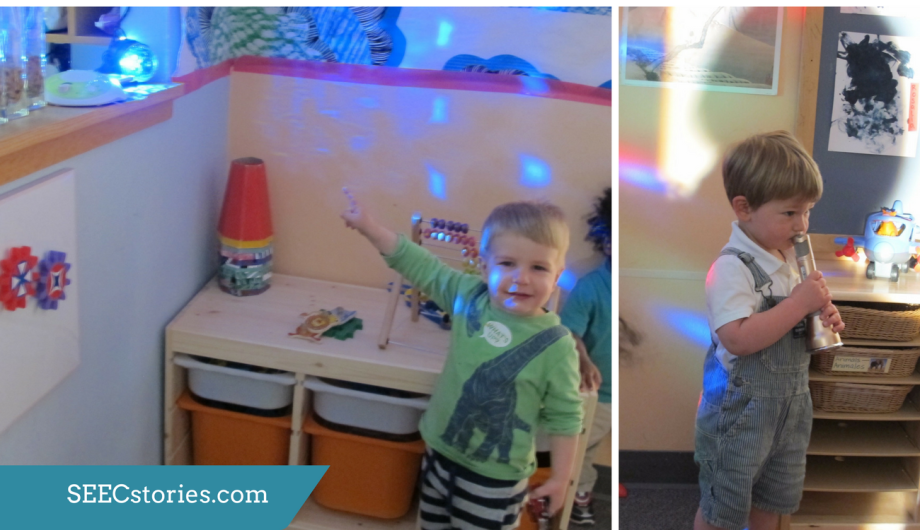
 Light was another topic that the teachers were hoping to explore with their class since karaoke performances often involve a light show. As part of the instillation of Snail Space color changing lights are projected onto the two canvas’ and floor space design. In addition to experiencing the light that is part of the performance of Snail Space, the teachers brought battery powered tea lights to allow the children to explore and manipulate their own light.
Light was another topic that the teachers were hoping to explore with their class since karaoke performances often involve a light show. As part of the instillation of Snail Space color changing lights are projected onto the two canvas’ and floor space design. In addition to experiencing the light that is part of the performance of Snail Space, the teachers brought battery powered tea lights to allow the children to explore and manipulate their own light.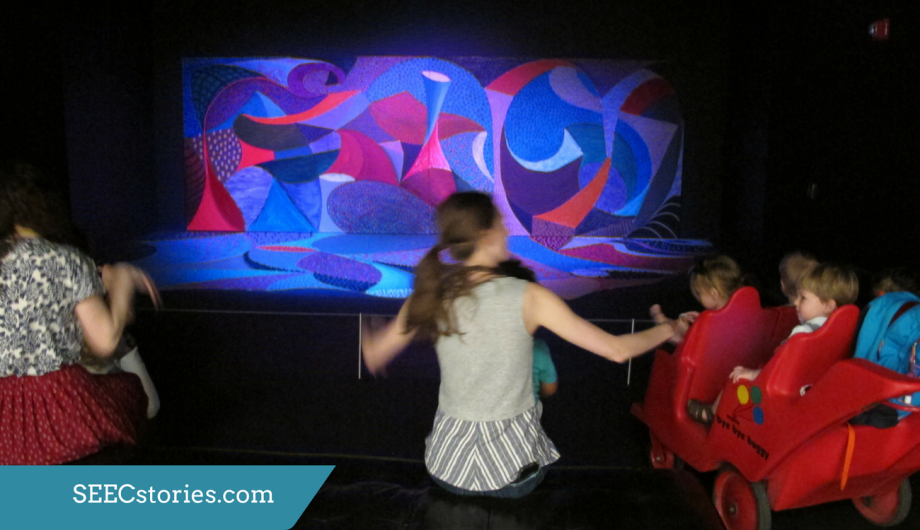



 On a recent trip to the Postal Museum, I was reacquainted with how perfect the National Postal Museum is for young children. Throughout the experience, there were two things that stuck out to me – hands-on objects and imaginative experiences.
On a recent trip to the Postal Museum, I was reacquainted with how perfect the National Postal Museum is for young children. Throughout the experience, there were two things that stuck out to me – hands-on objects and imaginative experiences. Within this small space there are a lot of opportunities for your child. The letter sorting is a fun way to spy a letter – V is for Virginia or D for DC. Caretakers can lift up children to allow little hands to practice placing the mail into the slots. It is also a great way for a few young children to build their team working skills. You might want to play a game of passing, sorting, and delivering envelopes from the train. You can even watch this
Within this small space there are a lot of opportunities for your child. The letter sorting is a fun way to spy a letter – V is for Virginia or D for DC. Caretakers can lift up children to allow little hands to practice placing the mail into the slots. It is also a great way for a few young children to build their team working skills. You might want to play a game of passing, sorting, and delivering envelopes from the train. You can even watch this  Though the bags in the exhibit are secured, a clever caretaker might bring a few small bags and give the children a chance to carry the bags or even compare weight — all of the sudden your visit into a STEM lesson! Those letter bags are also a great place to stop and do a simple sorting activity. You can sort blocks by colors or shapes to explain how the bags were used to sort mail by location. This a simple way to introduce some math too!
Though the bags in the exhibit are secured, a clever caretaker might bring a few small bags and give the children a chance to carry the bags or even compare weight — all of the sudden your visit into a STEM lesson! Those letter bags are also a great place to stop and do a simple sorting activity. You can sort blocks by colors or shapes to explain how the bags were used to sort mail by location. This a simple way to introduce some math too! Consider using the train as an anchor object to compare with other forms of transportation in the hall. With some Velcro and photos, you can create a visual timeline showing the progression of a carriage, train, plane, and truck. You can actually get inside the truck and steer – they will love it. Of course, you can also introduce your young child to the concept of mail and how it moves from one place to another. Its a great opportunity to have them help you compose a postcard to a loved one and then send it off.
Consider using the train as an anchor object to compare with other forms of transportation in the hall. With some Velcro and photos, you can create a visual timeline showing the progression of a carriage, train, plane, and truck. You can actually get inside the truck and steer – they will love it. Of course, you can also introduce your young child to the concept of mail and how it moves from one place to another. Its a great opportunity to have them help you compose a postcard to a loved one and then send it off.






















 students in your class.
students in your class. Our inaugural Object of the Month is actually not so much an object, but a gallery. The Rocks Gallery in the National Museum of Natural History is tucked at the back of the
Our inaugural Object of the Month is actually not so much an object, but a gallery. The Rocks Gallery in the National Museum of Natural History is tucked at the back of the 
